Plant Choices for Soil Stabilization through Permaculture
Soil erosion is a pressing global issue, affecting both our economy and environment. Understanding what causes erosion, such as water runoff, wind, and human actions like farming and deforestation, is crucial for preventing it.
In the fight against soil erosion, a holistic design approach is vital. This approach makes each part work together, creating a strong, lasting solution. In permaculture, for instance, groundcover plants like carpet verbena and fern cushions are used to control and prevent soil erosion. These plants form dense, durable carpets that protect the soil effectively, with deep roots and rapid growth.
Native plants, with their strong roots and ability to handle environmental stress, are great for controlling erosion because they fit well with local conditions and support local wildlife. They also create valuable habitats for wildlife along waterways. Willows and cottonwoods, popular choices for stem cuttings in bioengineering, are no exception.
Grasses and legumes are commonly used in mine reclamation and help improve soil quality. Bioengineering techniques, which use living plants and natural materials, are often cheaper and less disturbing than other methods, making them suitable for sensitive or steep sites. Fascines, brush mattresses, and living structures are common bioengineering methods.
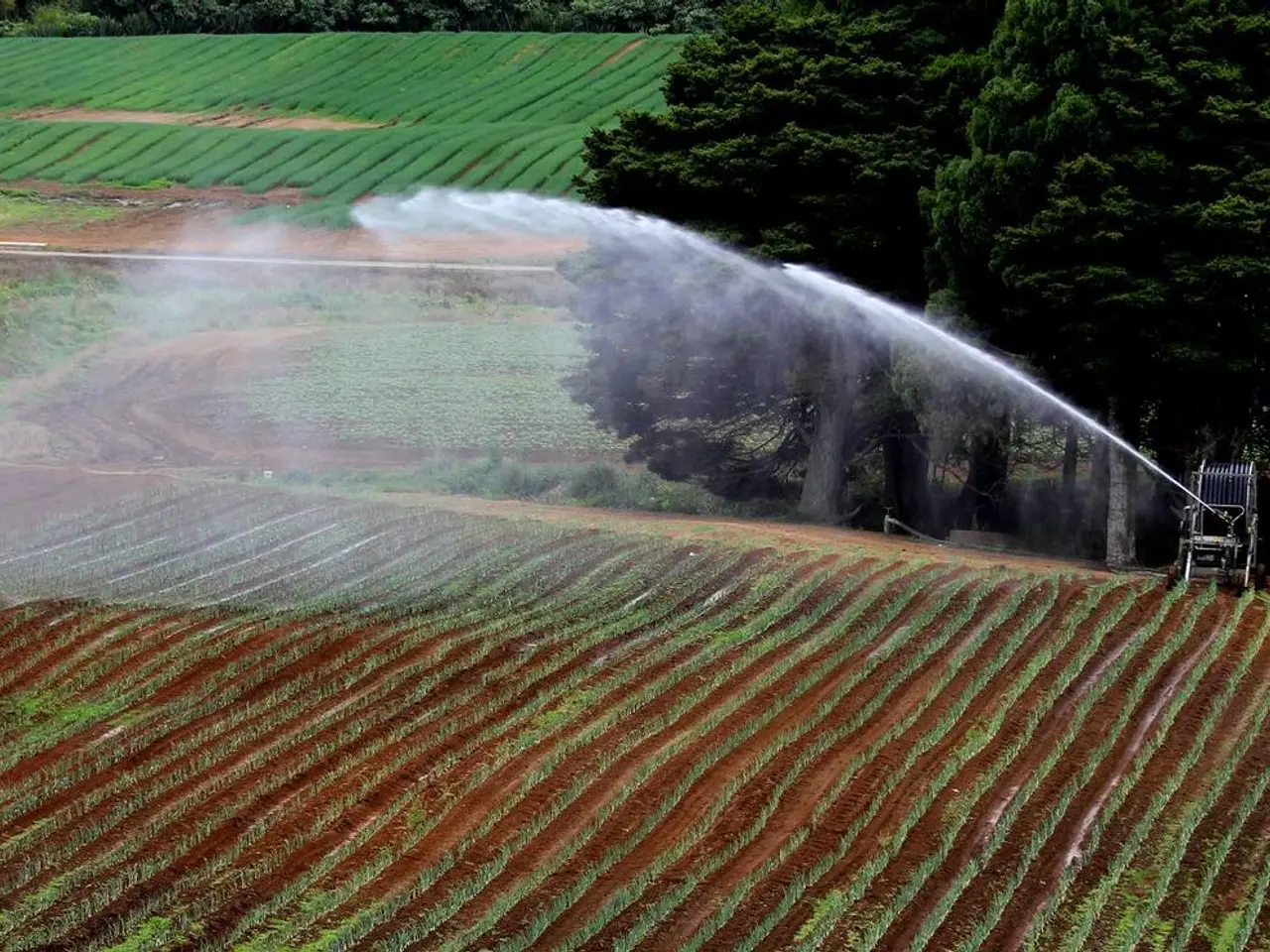
Effective stormwater management is not just about managing water flow; it's about preserving the integrity of our soil and protecting the health of our ecosystems. Permeable surfaces, rain gardens, and bioswales are effective strategies for fighting soil erosion. Using a mix of these strategies, we can create a resilient, sustainable landscape.
Sediment traps, silt fences, check dams, and vegetative filters are methods to stop soil from moving after disturbance. Revegetation, involving adding soil amendments and planting the right plants, is important for fixing eroded or damaged areas. Choosing the right erosion control plants, like ground covers, shrubs, and grasses, is essential for a multifaceted, integrated approach.
Integrating erosion control strategies includes using plants, structural interventions, and managing stormwater for long-term sustainability. Riparian buffers, which help stabilise streambanks and improve water quality, are a good example. They have been shown to reduce non-point source pollution by absorbing and filtering animal wastes, sediments, nutrients, and pesticides from crop and rangelands.
By combining various erosion control strategies, we can create a resilient, sustainable landscape that safeguards the soil and promotes the overall health of the ecosystem. Using the ideas from this article, we can help save our soil. Let's work together to combat soil erosion and build a more sustainable future.
Read also:
- Recognition of Exceptional Patient Care: Top Staff Honored by Medical Center Board
- A continuous command instructing an entity to halts all actions, repeated numerous times.
- Oxidative Stress in Sperm Abnormalities: Impact of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) on Sperm Harm
- Is it possible to receive the hepatitis B vaccine more than once?